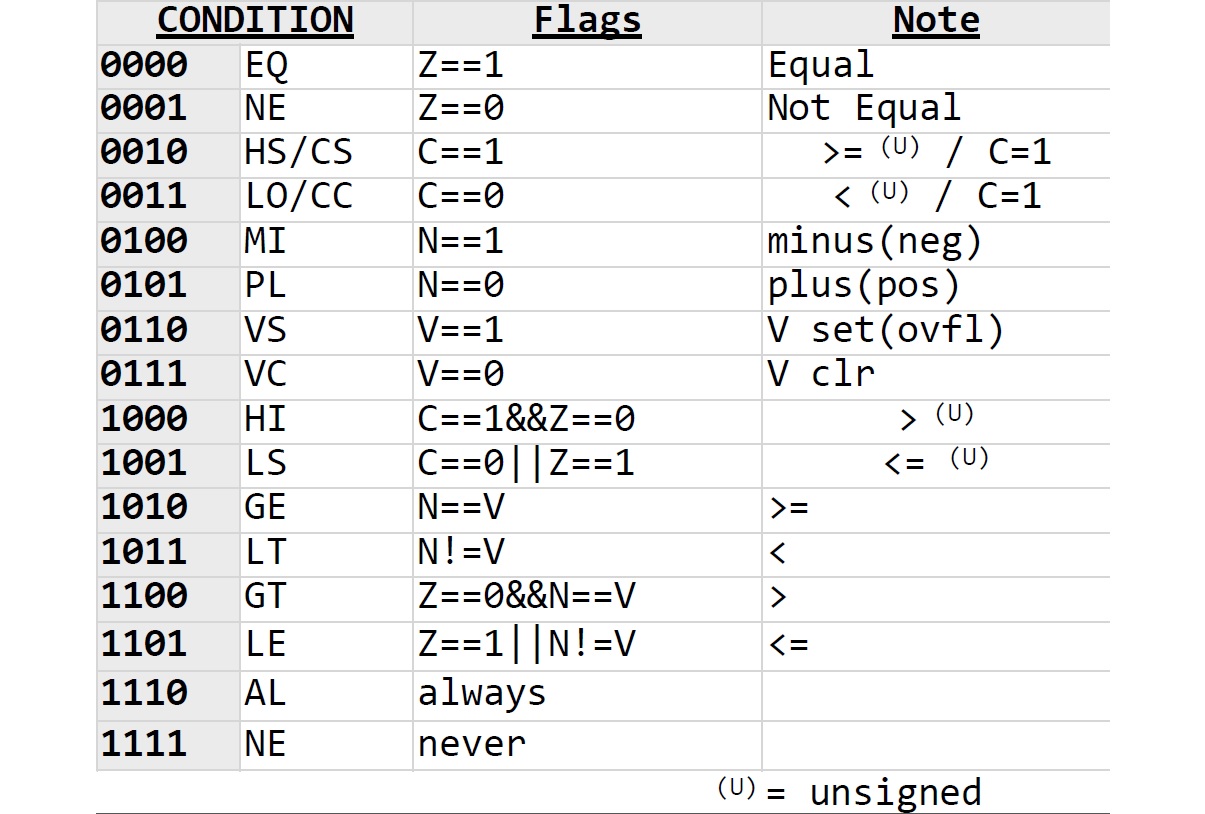
ARM Data-processing Instructions
Objectives
1. To investigate Arithmetic Operations and more other instructions. 2. To implement them in Keil uVision5.
ARM Registers and the Conventions of Use
As mentioned in the previous lab, ARM has 16 programmer-visiable registers
and a Current Program Status Register, CPSR.
Here is a picture to show the ARM register set.
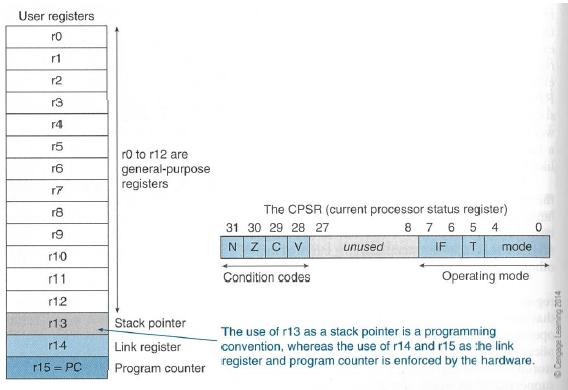
R0 to R12 are the general-purpose registers. R13 is reserved for the programmer to use it as the stack pointer. R14 is the link register which stores a subroutine return address. R15 contains the program counter and is accessible by the programmer. CPSR: current program status register (32 bit) Stores the status of the previous ALU operation. 4 flags N = 1, if result was negative Z = 1, if result was zero C = 1, if result had a carry-out V = 1, if result was an overflow These can be used to make decisions later on.Each ARM instruction is encoded into a 32-bit word. Access to memory is provided only by Load and Store instructions.
ARM data-processing instructions operate on data and produce new value.
They are not like the branch instructions that control the operation of the processor and sequencing of instructions.
ARM instructions have the following general format:
Label Op-code operand1, operand2, operand3 ; comment
Arithmetic Instructions
Arithmetic instructions are very basic and frequently used in your
ARM programming.
Here is a table that demonstrates the usage of the ARM
processor's arithmetic instructions with examples.
Instruction Mnemonic Meaning ======================================================================== Addition ADD R0, R1, R2 ; R0 = R1 + R2 ------------------------------------------------------------------------ Addition ADDS R0, R1, R2 ; R0 = R1 + R2, ; and FLAGs are updated ------------------------------------------------------------------------ Subtraction SUB R1, R2, R3 ; R1 = R2 - R3 ------------------------------------------------------------------------ Subtraction SUBS R1, R2, R3 ; R1 = R2 - R3, ; and FLAGs are updated ------------------------------------------------------------------------ SUBS R7, R6, #20 ; R7 = R6 - 20 ; Sets the flags on the result ------------------------------------------------------------------------ Reverse Subtraction RSB R4, R4, #120 ; R4 = 120 - R4 ------------------------------------------------------------------------ Multiply MUL R0, R1, R2 ; R0 = R1 * R2 ------------------------------------------------------------------------ Division SDIV R0, R2, R4 ; Signed divide, R0 = R2/R4 ------------------------------------------------------------------------ UDIV R8, R8, R1 ; Unsigned divide, R8 = R8/R1. ------------------------------------------------------------------------
Examples of Move Instructions
Mnemonic Meaning
------------------------------------------------------------------------
MOV R1, #0xFA05 ; Write value of 0xFA05 to R1, flags are not updated
------------------------------------------------------------------------
MOVS R11, #0x000B ; Write value of 0x000B to R11, flags get updated
------------------------------------------------------------------------
MOVS R10, R12 ; Write value in R12 to R10, flags get updated
------------------------------------------------------------------------
MOV R3, #23 ; Write value of 23 to R3
------------------------------------------------------------------------
MOV R8, SP ; Write value of stack pointer to R8
------------------------------------------------------------------------
MVNS R2, #0xF ; Write value of 0xFFFFFFF0 (bitwise inverse of 0xF)
; to the R2 and update flags.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Logical Operation Instructions
------------------------------------------------------------------------ AND R9, R2, R1 ; R9 = R2 AND R1 ------------------------------------------------------------------------ AND R9, R2, #0xFF00 ; R9 = R2 AND #0xFF00 ------------------------------------------------------------------------ ANDS R9, R8, #0x19 ; flags get updated ------------------------------------------------------------------------ ORR R9, R2, R1 ; R9 = R2 OR R1 ------------------------------------------------------------------------ ORR R9, R2, #0xFF00 ------------------------------------------------------------------------ EOR R7, R11, R10 ; R7 = R11 XOR R10 ------------------------------------------------------------------------ EORS R7, R11, #0x18181818 ; flags get updated ------------------------------------------------------------------------ BIC R0, R1, #0xab ; R0 = R1 AND (NOT(#0xab)) ------------------------------------------------------------------------
Conditional Execution of Instructions
Each ARM instruction is encoded into a 32-bit word.
The basic encoding format for the instructions such as
Load, Store, Move, Arithmetic, and Logic instructions, is as follows:
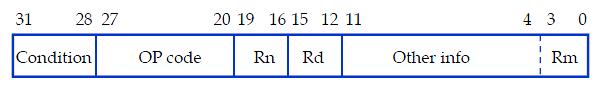
An instruction specifies a conditional execution code
(Condition), the OP code, two or three registers (Rn, Rd,
and Rm), and some other information.
Here is a more detailed description.
All the ARM instructions are conditionally executed depending on a condition specified in the instruction(bits 31-28).
- The instruction is executed only if the current state of the
processor condition code flag satisfies the condition
specified in bits b31-b28 of the instruction.
For example: CMP R0, #25 ; flags are updated according to (R0 - #25) ADDGT R1, R2, #12
- The instructions whose condition does not meet the processor condition code flag are not executed.
- One of the conditions is used to indicate that the instruction is always executed.
Examples of Shift Instructions
------------------------------------------------------------------------ LSL R4, R5, #2 ; Logical shift left by 2 bits ------------------------------------------------------------------------ LSR R4, R5, #6 ; Logical shift right by 6 bits ------------------------------------------------------------------------ LSLS R1, R2, #3 ; Logical shift left by 3 bits with flag update ------------------------------------------------------------------------ ROR R4, R5, R6 ; Rotate right by the value in the bottom byte of R6 ------------------------------------------------------------------------ RRX R4, R5 ; Rotate right with extend (one bit only). ------------------------------------------------------------------------Here is a link for your references:
Cortex-M3 Devices Generic User Guide. Section 3.5 and 3.6.
An Example of Using Arithmetic Instructions
;The semicolon is used to lead an inline documentation
;
;When you write your program, you could have your info at the top document block
;For Example: Your Name, Student Number, what the program is for, and what it does etc.
;
; This program will catculate the value of the following function:
; f(x) = 5x^2 - 6x + 8 when x = 7.
;
;;; Directives
PRESERVE8
THUMB
; Vector Table Mapped to Address 0 at Reset
; Linker requires __Vectors to be exported
AREA RESET, DATA, READONLY
EXPORT __Vectors
__Vectors
DCD 0x20001000 ; stack pointer value when stack is empty
DCD Reset_Handler ; reset vector
ALIGN
; The program
; Linker requires Reset_Handler
AREA MYCODE, CODE, READONLY
ENTRY
EXPORT Reset_Handler
Reset_Handler
;;;;;;;;;;User Code Start from the next line;;;;;;;;;;;;
MOV R0, #7 ; x = 7
MUL R1, R0, R0 ; R1 = x^2
MOV R4, #5
MUL R1, R1, R4
MOV R5, #6
MUL R2, R0, R5 ; R2 = 6x
SUB R3, R1, R2 ; R3 = 5x^2 - 6x
ADD R3, R3, #8 ; R3 = 5x^2 - 6x + 8
ALIGN
STOP
B STOP
END ; End of the program
Load and Store Instructions
To access memory, we can only use Load and Store instructions.
LDR dest, expression
LDR R6, [R4] ; load R6 with the value in the memory whose address is in R4
STR STR{cond} srce,[base],offset
STR R0,[R1] ; store R0 in the byte address R1
STR R0,[R1,#20] ; store R0 in the byte address R1+20
STR R0,[R1,R2,LSL#2] ; store R0 in the address given by R1+R2*4
Examples:
LDR R0, NUM ; load R0 with the value of NUM in memory
LDR R6, = NUM ; Load the address of NUM to R6
MOV R0, #0x001C ; Load the value to the R0
STR R0, [R6] ; Store the value in R0 to NUM
Another Example
;The semicolon is used to lead an inline documentation
;When you write your program, you could have your info at the top document block
;For Example: Your Name, Student Number, what the program is for, and what it does etc.
;
; See if you can figure out what this program does
;
;;; Directives
PRESERVE8
THUMB
; Vector Table Mapped to Address 0 at Reset
; Linker requires __Vectors to be exported
AREA RESET, DATA, READONLY
EXPORT __Vectors
__Vectors
DCD 0x20001000 ; stack pointer value when stack is empty
DCD Reset_Handler ; reset vector
ALIGN
;Your Data section
;AREA DATA
SUMP DCD SUM
NUM1 DCD 5
NUM2 DCD 7
; The DCD directive allocates one or more words of memory,
; aligned on four-byte boundaries,
; and defines the initial runtime contents of the memory.
;
; For example, data1 DCD 1,5,20
; Defines 3 words containing decimal values 1, 5, and 20
AREA MYRAM, DATA, READWRITE
SUM DCD 0
; The program
; Linker requires Reset_Handler
AREA MYCODE, CODE, READONLY
ENTRY
EXPORT Reset_Handler
Reset_Handler
;;;;;;;;;;User Code Start from the next line;;;;;;;;;;;;
LDR R1, NUM1
LDR R2, NUM2
MOV R0, #0
ADD R0, R1, R2
SUBS R0, R0, #1
LSLS R3, R0, #2 ; Logical shift left by 2 bits with flag update
LDR R4, SUMP
STR R3, [R4]
LDR R6, [R4]
ALIGN
STOP
B STOP
END
Lab Assignment
![]() Copyright: Department of Computer Science, University of Regina.
Copyright: Department of Computer Science, University of Regina.